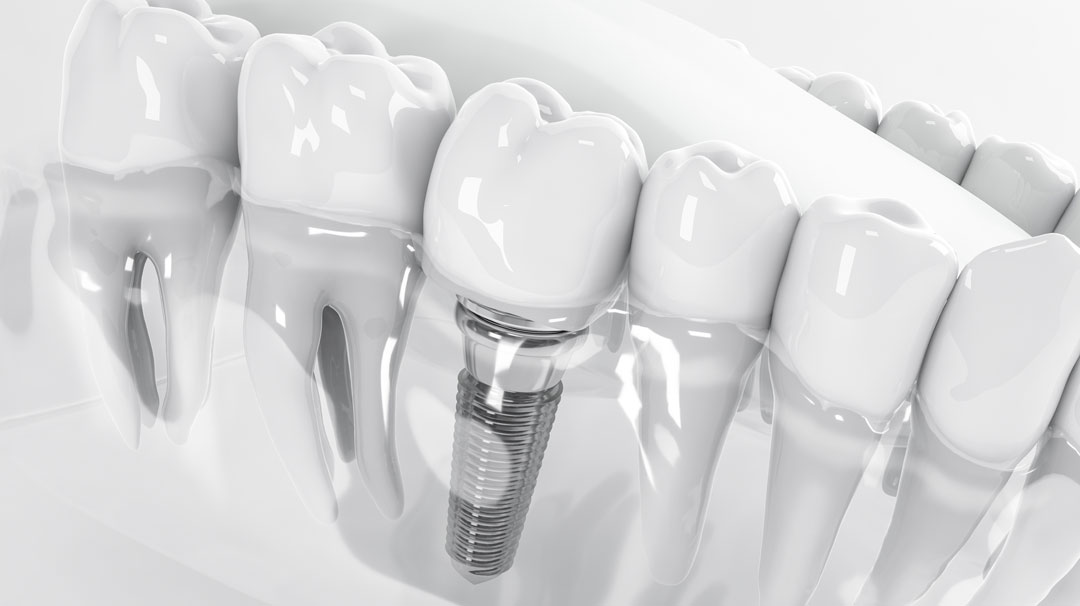
Dental implants serve as artificial replacements for lost natural teeth, effectively restoring their functionality. These implants consist of titanium screws inserted into the jawbone. Once in place, dental prosthetics are affixed onto these screws.
Implant treatments offer an advantage over other prosthetic options, as they don’t negatively impact neighboring teeth. Unlike standard fixed prosthetics, the adjacent teeth do not require alteration. Acting as root substitutes, implant teeth allow you to eat comfortably, articulate clearly, and confidently express yourself with a smile.
The Procedure of Implant Application
The application of dental implants involves a comprehensive examination and X-rays. In our clinic, we employ digital dental radiography, a method known for its speed and accuracy.
As previously mentioned, an implant comprises two components: the root piece placed within the jawbone and the top piece, which is the dental prosthesis attached to the root. The patient is first administered local anesthesia. After removing a non-functional tooth, a socket is created in the resulting gap. This socket provides the entry point for the root piece. Adequate time is required for the root piece to seamlessly integrate with the jawbone and gum tissue. Although this duration varies from patient to patient, an average timeframe of 3 to 5 months is typically expected.
Throughout this period, the patient temporarily goes without a tooth. Once this timeframe elapses and assuming the fusion between the titanium root piece and the bone is successful, the process of placing the dental prosthesis can commence.
Eligibility for Implant Treatment
Dental implants can be applied to individuals of all ages beyond childhood. However, young individuals must have completed their bone development. Typically, this is reached around 16-17 years for girls and 18 years for boys. Nevertheless, implant procedures are more commonly sought by older individuals. This demographic tends to experience greater tooth loss and jawbone degradation than younger individuals, thereby requiring a higher demand for dental implants.
Key Considerations
Certain physical conditions, hindrances, and medical conditions can complicate implantation. Examples include heart conditions, rheumatic diseases, diabetes, and blood clotting disorders. Additionally, situations where the anatomical structure of the jawbone is inadequate or when the patient experiences psychological reactions such as anxiety and significant fear towards surgical procedures can complicate the implantation process.